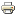
Prediction of Low Frequency Response
Finite Element Modelling is used to model the physical loudspeakers coupled to the volume of air contained within the car cabin. The wave-based technique means that the modal field and diffraction effects at low and mid-frequencies are captured and results can be visualised in both the frequency and time domain.
A model of a car interior was prepared. This was broadly based on a Volkwagen Passat B6 which was available for measurement, but differs significantly in terms of the interior trim detail which was too complex to accurately capture without access to the manufacturers CAD data. Any comparison between the model and measurement would therefore have differences attributable to the geometry in addition to unknown boundary impedances, leaks etc., but it is useful to examine experimental data to evaluate the potential value of simulation models should better data become available.
Loudspeakers Defined as Pistons in Doors. Mics located each side of simplified heads.
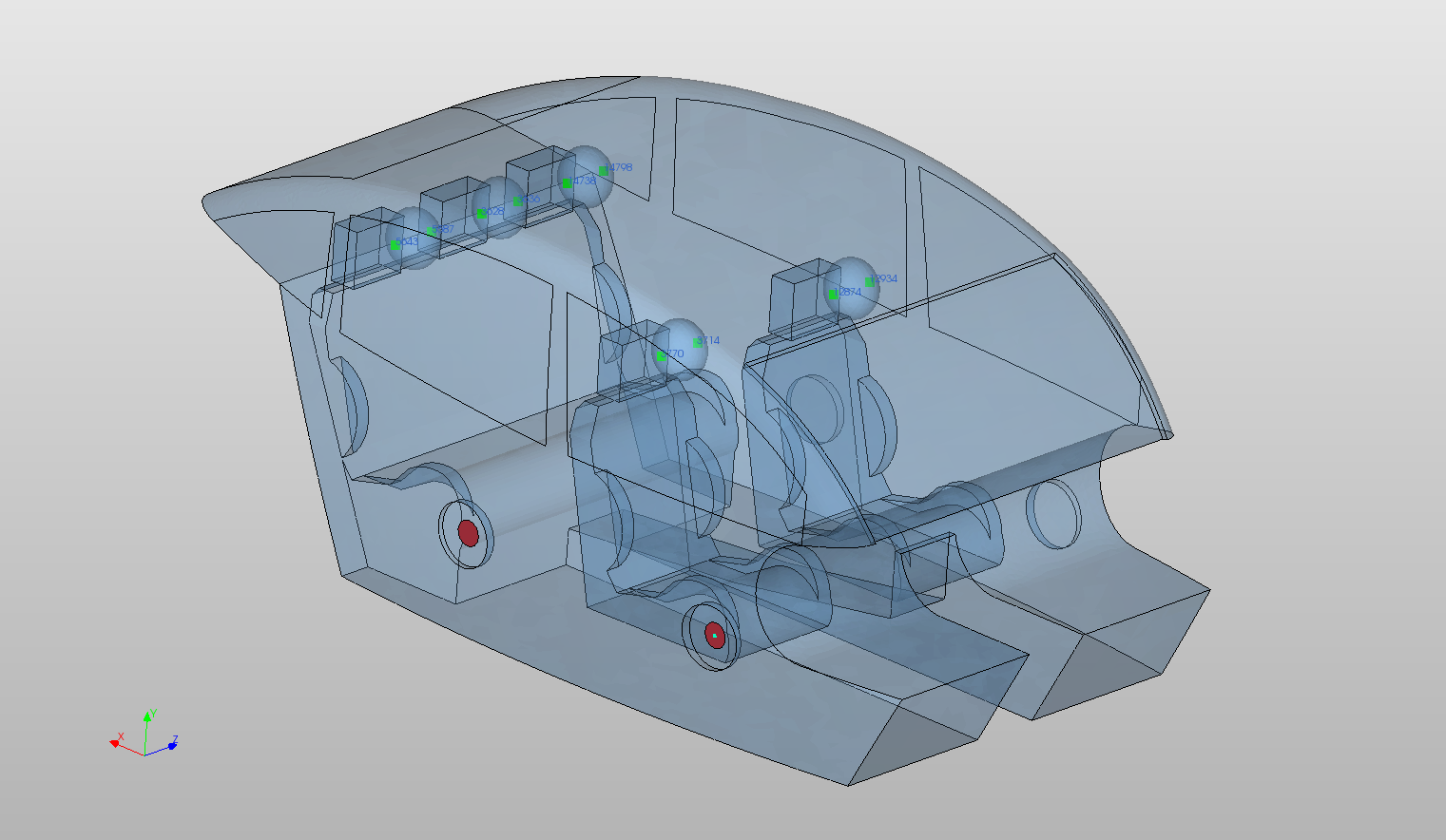
Windows Added as Flexible Structural Parts Coupled to Interior Air
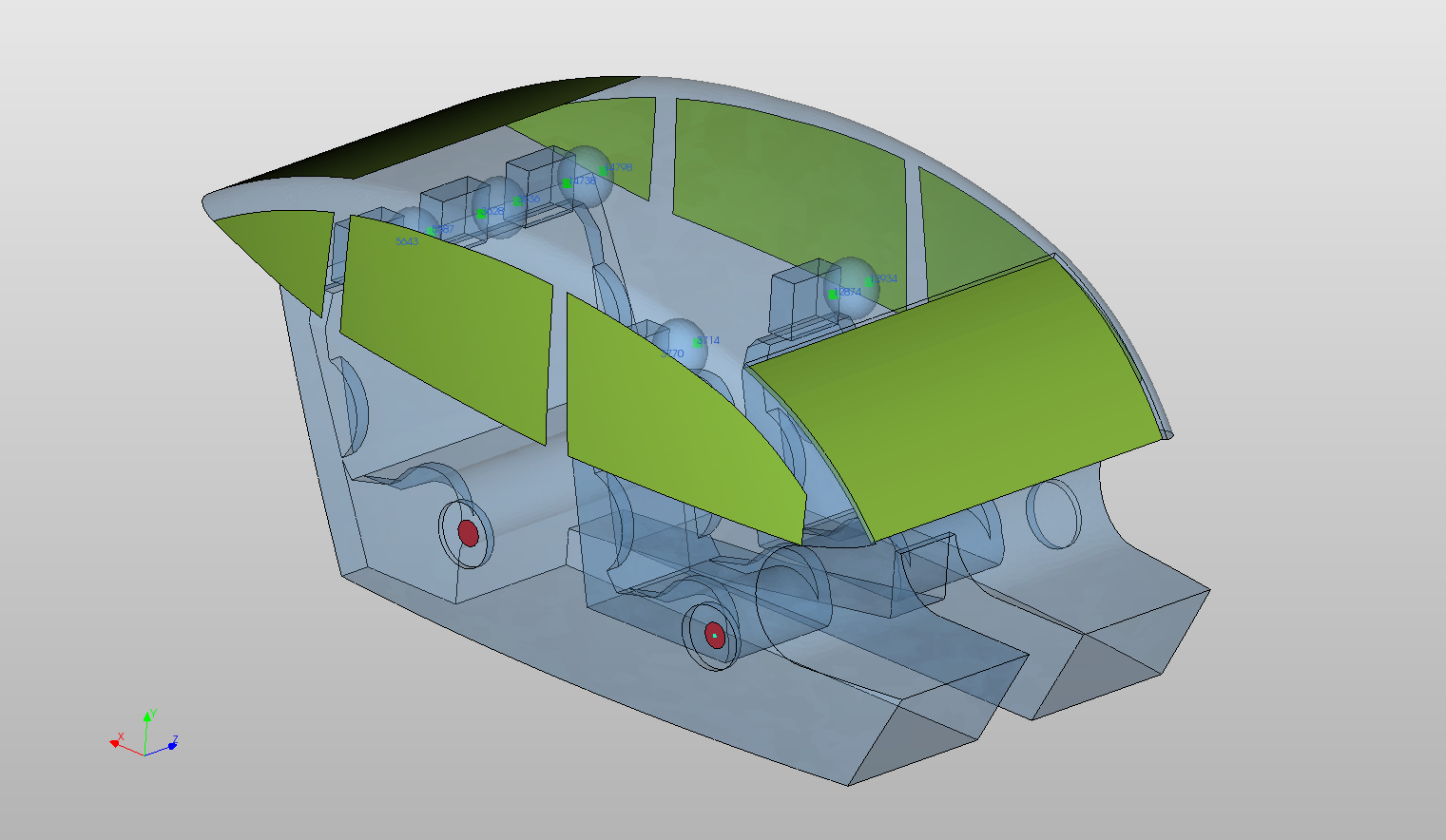
Surface Impedance Defined as a "Trial" Condition on Carpets, Seats and Headliner
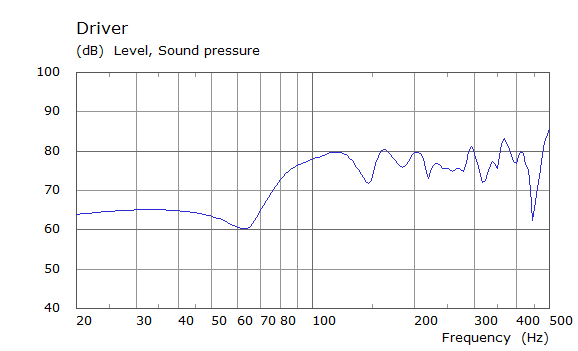
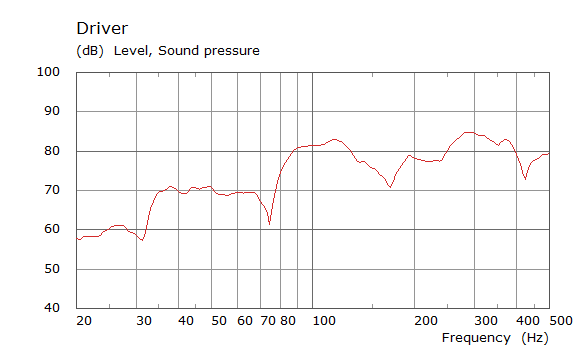
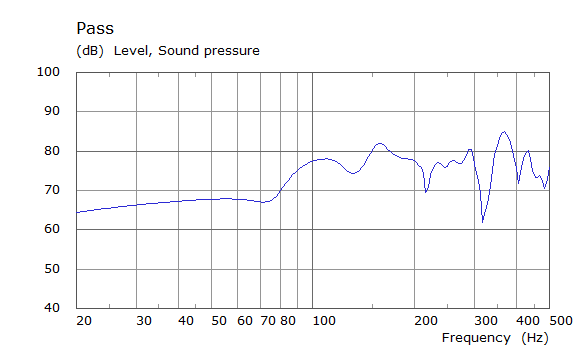
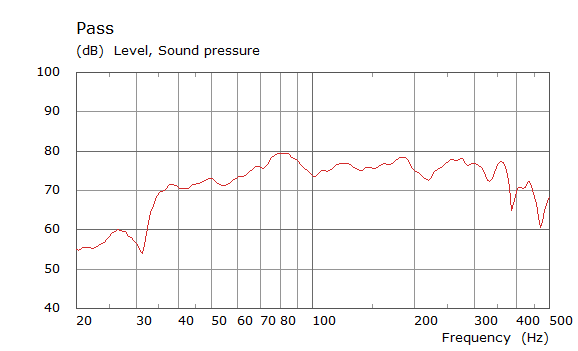
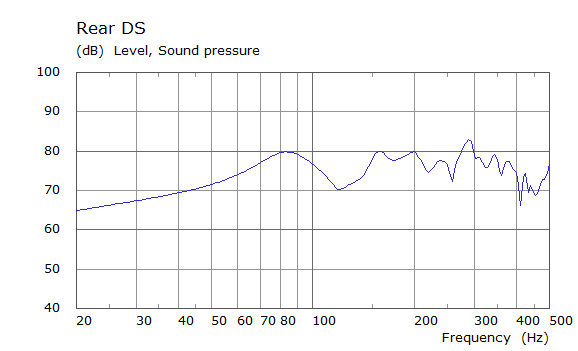
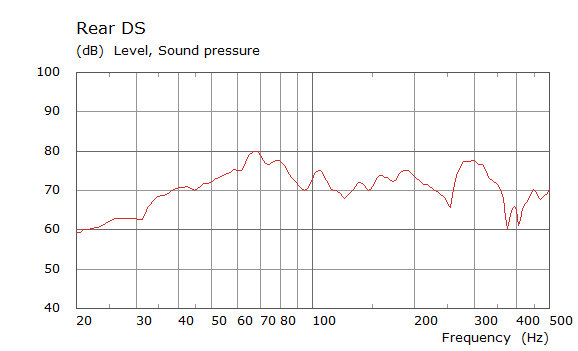
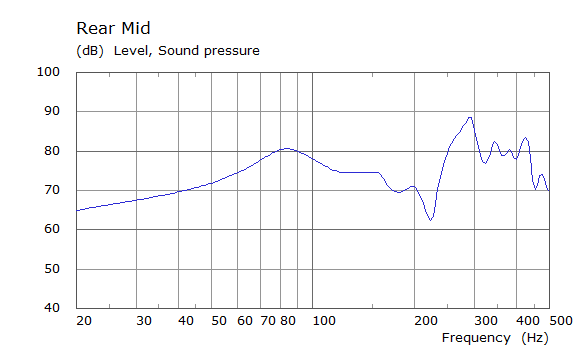
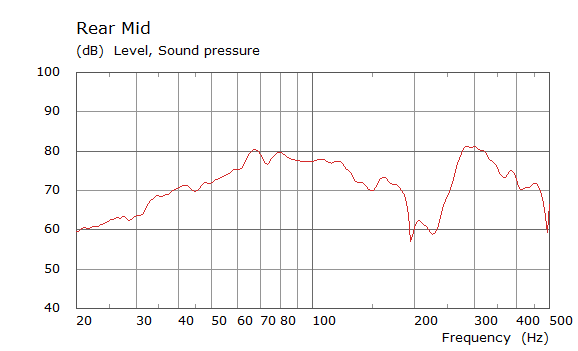
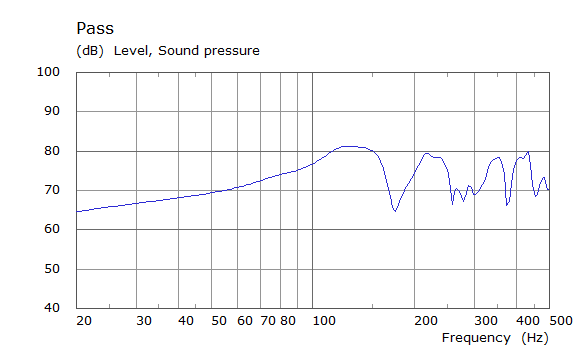
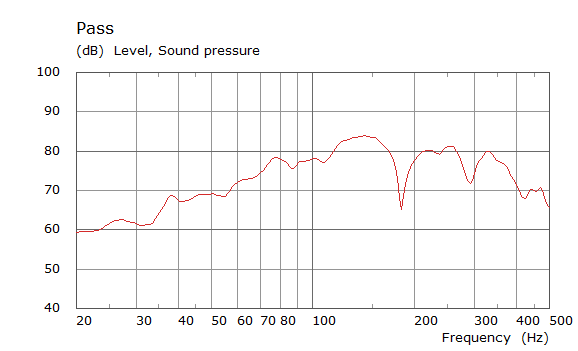
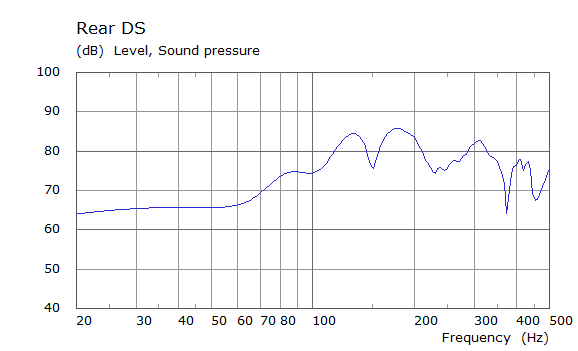
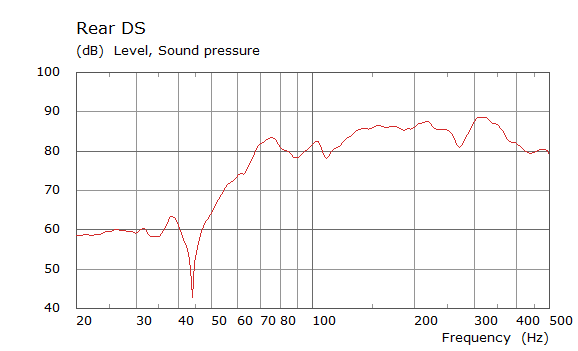
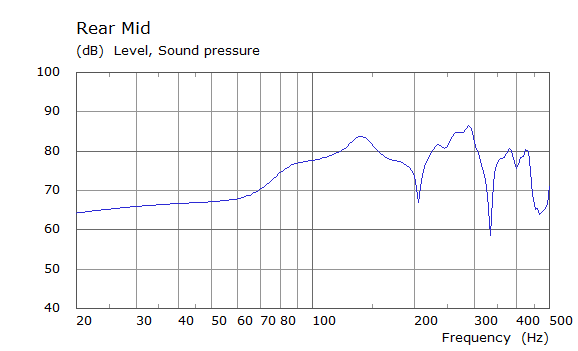
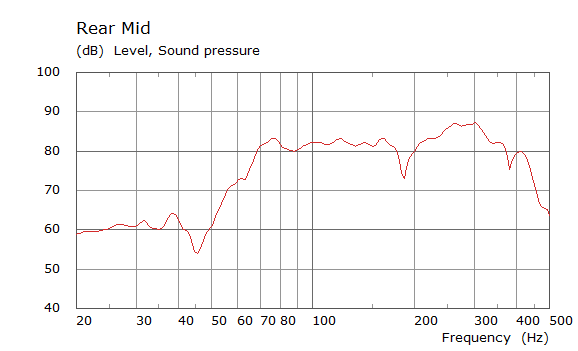
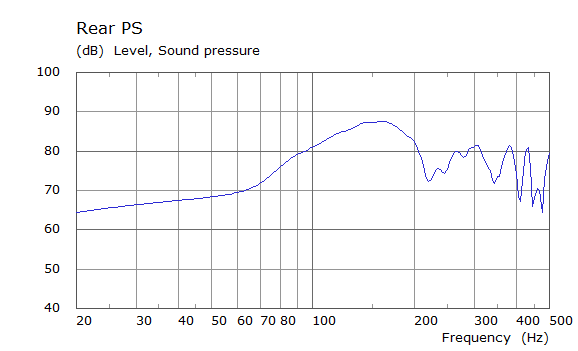
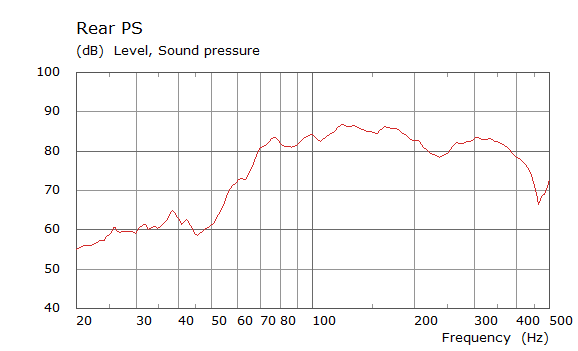
Comparison Between Measured and Simulated Frequency Responses
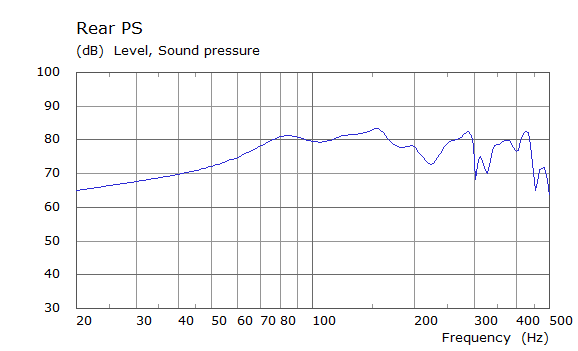
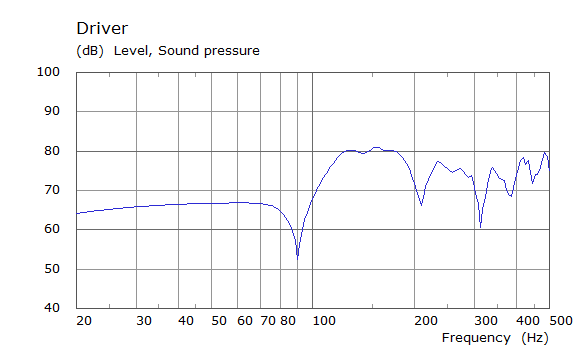
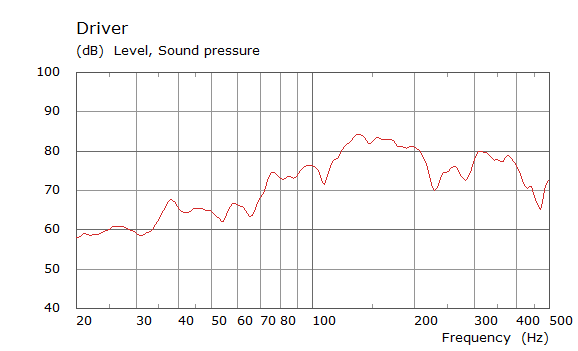
The curves below are based on the average of left and right "ear" responses for each seat position. In the experimental case, a dummy head with microphones at the ear locations was used to capture the data.
Front Driver Position Door Loudspeaker Only, All Seating Positions
| Simulated | Experimental |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
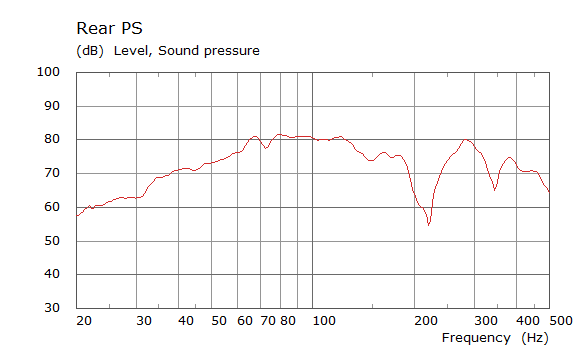 |
Rear Driver Position Door Loudspeaker Only, All Seating Positions
| Simulated | Experimental |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |